|
|
|
|
|
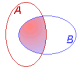
Probes common to both groups |
|
The resultant set contains probes that are common
to both probe groups. Use this type of comparison when you want to determine
the overall and specific similarities between two probe groups. |
|
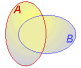
Probes from both groups |
|
The resultant set contains a non-redundant set of
all probes. That is, all probes are included from both groups with any
duplicates removed. |
|
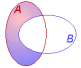
Probes from first group only |
|
The resultant set contains probes that are contained
only in probe group A and not in B. |
|
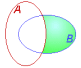
Probes from second group only |
|
The resultant set contains probes that are contained
only in probe group B and not in A. |