Create mutagenesis oligo sets (wizard) |
|
This wizard leads you through the creation of mutagenesis oligo set(s) based on a target DNA sequence that you enter or upload. A mutagenesis oligo set is a group of DNA oligonucleotides that is created from the application of one or more mutational strategies to a selected mutational region in a given target DNA sequence. For details, see Overview of working with mutagenesis oligo sets. You can then include selected mutagenesis oligo sets in a custom mutagenesis library. A mutagenesis library can be used to create variant forms of targeted proteins for a variety of experimental applications. See Learn about mutagenic oligos and mutagenesis libraries.
Another wizard is available in eArray that you can use to create a mutagenesis library based on a target DNA sequence that you enter. That wizard also creates mutagenesis oligo sets. See Create library for target sequence (wizard).
You must have a target cDNA sequence to which you want to apply mutations. The target sequence must be the coding strand of the DNA in 5' to 3' orientation, and it must be from 110 to 50,000 nucleotides in length. When you enter the sequence in step 2 of the wizard, you can upload the sequence from a FASTA file, or paste the sequence from another program. If you paste the sequence, do no include any descriptive text or non-DNA characters.
If you want to use the QuikCombine mutational strategy on a particular mutational region (see Overview of mutational strategies), prepare a file that defines the desired changes.
Once you start the wizard, the wizard leads you through several steps, summarized below. For detailed instructions for a specific step, click its name.
Step 1 – Define oligo set – In this step, you enter the name that eArray uses to identify this particular instance of the Create Mutagenesis Oligo Sets wizard. You can also enter descriptive information.
Step 2 – Input Target Sequence – In this step, you enter the target DNA sequence to which mutations are to be designed, and translate the target sequence into a sequence of amino acids. To help you find regions of interest, this step also lets you search the translated sequence by amino acid string or by position. You also define the mutational regions in the translated sequence to which you want to design oligo sets.
Step 3 – Review Primer Pair – In this step, you inspect the PCR primer sequences for each mutational region. PCR primers are used later with the QuikChange Oligo Library Mutagenesis System to amplify the oligos in a mutagenesis library. You can go back and redefine mutational regions if necessary, and create a new set of PCR primers.
Step 4 – Define Mutation – In this step, you select a mutational strategy to apply to each mutational region that you defined. eArray designs an oligo set for each region.
Step 5 – Oligo Set Summary – In this step, you can view each
of the mutagenesis oligo sets that were designed. You can then either
save them to your eArray account, or go back and re-define the mutational
strategies and/or regions.
Set
the application type to Mutagenesis.
The Home tab of the Mutagenesis application type appears.
In the Library
Wizards pane on the right side of the screen, select Create Mutagenesis Oligo Sets, then
click Next.
The first step of the wizard appears. As you go through the steps of
the wizard, click Next to
go to the next step. To go back to a previous step of the wizard,
click Back (if available).
At any time you can click Close
to close the wizard. eArray allows you to continue the wizard at a
later time.
In this step of the wizard, you enter the name of the library and any optional descriptive information.
In the Oligo Set Name field, type in a name for the oligo set.
If desired, type a description of
the oligo set into the Description
field.
This can be useful if you close the wizard, and later continue your
work.
Click Next.
The next step of the wizard appears.
In this step of the wizard, you enter the target cDNA sequence and translate it into a sequence of amino acids. You also define the desired mutational regions, which are the segments of the amino acid sequence to which you want to apply mutations.
Note: The cDNA sequence that you enter at this step must the coding strand in the 5' to 3' orientation, and it must be between 110 and 50,000 nucleotides long. Do not include any descriptive text or non-DNA characters. The first 30 nucleotides and the last 30 nucleotides are needed for PCR primer annealing and cannot be included in a mutational region.
Complete the fields in the Input Target Sequence pane:
Sequence Name: Type in a name for the target sequence (maximum 15 characters). eArray uses this name as the base for naming all the mutational regions that you will later define for the target sequence.
Enter the Target Sequence Below: Paste in the desired target cDNA sequence, or click Upload to upload the sequence from a FASTA file. If you paste the sequence, do not include any descriptive text or non-DNA characters.
Reading Frame: Select the reading frame for eArray to use when translating the cDNA sequence into an amino acid sequence. Select 1 to start the reading frame at nucleotide 1, select 2 to start at the reading frame at nucleotide 2, and select 3 to start the reading frame at nucleotide 3.
Click Translate.
eArray translates the sequence using the designated reading frame.
The program ignores any stop codons in the sequence and continues
translation through the entire sequence.
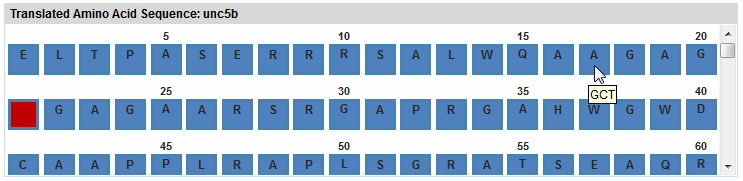
The translated sequence is displayed in the Translated
Amino Acid Sequence pane. See the image below for an example.
The first start codon appears in green, and stop codons appear in
red. All other codons appear in blue. The one or two DNA nucleotides
that may remain untranslated on either end of the sequence appear
as plain text. For the rest of the wizard, all positions that you
enter or that eArray displays refer to the amino acid positions in
this pane.

If desired, you can use the translated amino acid sequence to perform the following tasks:
To search for a specific amino acid sequence within the translated sequence:
Below the Translated Amino Acid Sequence pane, select AA Sequence from the Search drop-down list.
Type the desired sequence
into the adjacent field (20 amino acids maximum). Use the one-letter
amino acid code. Separate multiple search terms with commas.
Example
search strings
Click Find.
If eArray finds the search term(s) in the sequence, it highlights all
matching instances and scrolls the amino acid sequence to the location
of the first match. To ensure that you see all matches, scroll through
the entire sequence.
To search for a specific amino acid position within the translated sequence:
Below the Translated Amino Acid Sequence pane, select AA Position from the Search drop-down list.
Type the desired position
or position range into the adjacent field. Separate multiple search
terms with commas.
Example
search strings
Click Find.
If eArray finds the search term(s) in the sequence, it highlights all
matching instances and scrolls the amino acid sequence to the location
of the first match. To ensure that you see all matches, scroll through
the entire sequence.
To download the translated sequence:
Below the Translated
Amino Acid Sequence pane, click Download
Translated Amino Acid Sequence.
A dialog box opens providing prompts on downloading the sequence. These
prompts vary depending on your internet browser.
Follow the prompts to
complete the download.
The downloaded file is a FASTA
format file.
In the Define
Mutational Regions pane, follow the steps below to define at
least one range of amino acid positions to which to apply mutations.
When you define a mutational region, you only define a range of amino
acids to which changes will be applied. You select the actual mutational
strategy in the next step of the wizard.
In
the text box under Region,
type a range of amino acids to which you want to introduce mutations.
A given mutational region must be at least 17 amino acids long
and cannot include the first 10 amino acids or the last 10 amino
acids in the translated sequence.
Example: A range of 40-82 selects the amino acid region
from position 40 to position 82 in the translated sequence.
Note:
•
If you intend to define only one mutational region, it
must be 1000 amino acids in length or shorter.
•
If you intend to create multiple mutational regions, the
total number of amino acids across all regions cannot
exceed 1000.
•
Mutational regions cannot overlap.
•
eArray lets you include stop codons in mutational regions;
however, the mutational strategy that you select in step
5 of the wizard may replace stop codons with codons that
specify amino acids.
•
In step 4 of the wizard, you will have the opportunity
to protect specific amino acid positions from mutation.
Click Create.
eArray adds an entry to the list of mutational regions. If the
region you entered is longer than 50 amino acids, eArray automatically
divides the region into smaller, contiguous "child"
mutational regions that are all 50 amino acids in length or shorter.
If desired, repeat steps a and b
to create additional mutational regions.
You can define up to 20 mutational regions of 50 amino acids or
less.
If you define a mutational region in error, mark the check box
next to its name, then click Delete.
Click Next.
The next step of the wizard appears.
This step of the wizard displays
a table of the PCR primers that eArray has designed to amplify the mutational
regions you defined in the previous step. When you request
a quote, you will need to order the PCR primers in this table from
your preferred supplier of primers. Agilent does not supply the primers
in the QuikChange Oligo Library Mutagenesis System. The table shows the
primer sequences for each mutational region and child mutational region
as well as the length, melting temperature (Tm), and GC percentage (%GC)
for each primer.
The Homopolymer Run column will
list "positive" for any primer with a run of 7 identical nucleotides
in a row. Primers listed as "false" do not contain runs of homopolymers.
In the Mutational Region column,
any regions listed in red have been flagged by eArray as potentially problematic
for PCR. Allow the cursor to hover over the name of the mutational region
to view the warning.
In this step of the wizard, you select and configure the desired mutational strategy (or strategies) for each mutational region that you defined in the previous step of the wizard. All mutational regions must have at least one mutational strategy assigned. For more information about mutational strategies, and examples, see Select a mutational strategy.
Under Select Mutation Strategy, select the desired strategy from the Strategy drop-down list. Follow one of the further sets of instructions below depending on the chosen strategy:
If you selected QuikScan1:
In
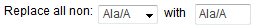
the fields labeled Replace all
non: [ __ ] with [ __ ], select the amino acid that you
want to use to individually replace all other amino acids in a
mutational region. For example, with the selections shown in the
image below,eArray will design a set of oligos to replace all
non-alanines with alanines.
In
the fields labeled Replace all
wild type: [ __ ] with [ __ ], you can select to replace
the positions that already code for the replacement amino acid
with a different amino acid. To leave those positions unchanged,
leave the default of N/A
in the second field. With the selections shown in the image below,
eArray will design an oligo set to replace each wild type alanine
with a glycine.

In
the Protect Position box,
you can enter the amino acid position numbers of any amino acids
that you do not want to alter. Separate multiple positions with
a comma and do not include spaces. In the image below, the amino
acids at positions 14 and 62 have been designated for protection.

If you selected QuikScan19:
eArray
will design a set of oligos to replace each amino acid in the
selected mutational region(s) with all other 19 possible amino
acids. You need only enter the amino acid position numbers of
any amino acids that you do not want altered. Separate multiple
positions with a comma and do not include spaces. In the image
below, the amino acids at positions 14 and 62 have been designated
for protection.

If you selected QuikCombine:
Upload a text file (with file extension txt) that designates the positions of the amino acid you want to mutate and the new amino acids you want to replace them with. Click Browse to open the File Upload dialog box, then browse to the location of the file and click Open. The file must follow a specific format (see Examples), and you need to upload a separate file for each mutational region that you want to mutate using the QuikCombine strategy.
Using
the check boxes under Mutation
Type, select how you want to combine the site-specific
mutations designated in the uploaded file. The options are described
below. You can select more than one check box.
Single – eArray designs
oligos to generate each mutation individually. The variant proteins
that are created each contain only one mutation.
Double – eArray designs
oligos to create variant proteins that each contain 2 of the designated
mutations. All possible combinations of double mutants are generated.
Triple – eArray designs
oligos to create variant proteins that each contain 3 of the designated
mutations. All possible combinations of triple mutants are generated.
Quadruple – eArray designs
oligos to create variant proteins that each contain 4 of the designated
mutations. All possible combinations of quadruple mutants are
generated.
Under Select Mutational Regions, mark the mutational regions to which to apply the mutational strategy. For the QuikScan1 and QuikScan19 strategies, you can select multiple mutational regions at a time.
Note: Because all mutational regions must have one mutational strategy assigned, you must remove any mutational regions that remain unused after you define all mutations. To remove unused regions, click Back to go back to the previous step in the wizard and delete the unused regions.
Under Define Host Type, select the following parameters.
In the drop-down list, select the type of host that you will be using for expression of the mutant proteins. eArray supports E. coli, yeast, mammalian, and insect host types. This selection helps eArray optimize codon usage for mutations for the intended host.
Under Codon
Preference, select the type of codon usage for eArray to
use when designing the mutagenic oligos:
Preferred – Use the codons
that are preferred for your chosen host type. You can click View
to see a list of the preferred codon usages.
Custom – Designate a custom
codon usage. Click Edit
to open the preferred codon usage table and make the desired edits.
The preferred codon for each amino acid is marked by default.
If you selected the QuikScan1 or QuikScan19 strategy, you can
select up to 2 codons for each amino acid. If you selected the
QuikCombine strategy, you can select 1 codon for each amino acid.
When you are done making edits, click Submit.
Note: If you select 2 codons for a single amino acid, whenever the mutagenesis strategy calls for mutating the wild type amino acid to the amino acid with 2 codon designations, eArray generates separate mutagenic oligos for each codon.
Click Create
Mutation.
The information on the mutational region/mutational strategy pairs
that you defined appears in the table in the Mutations
pane.
If desired, you can view the amino acid sequence of the mutational
region, with mutated positions noted, by clicking Edit
in the Actions column of the
table. Click Delete to delete
any of the mutations in the table.
In the same manner, define any additional mutations. Every mutational region must have one strategy applied to it.
When you are finished defining mutations, click Next to advance to the next step in the wizard.
When you advance to this step of the wizard, eArray processes the mutations you defined in the previous step and designs the oligo sets. Each oligo set contains the mutagenic oligos for a single mutational region/mutational strategy pair. The oligo sets are listed in the Oligo Sets pane, and are named according to the mutational region and mutational strategy. If desired, you can view the oligos in a set.
Click
the oligo set name.
A new window opens displaying details on the oligos and oligo set including
oligo sequences.
Click Close to close the window.
When you have finished
reviewing and editing the library layout, click Save
to save the oligo sets and close the wizard.
The oligo sets are now available in your eArray account. You can use
them to create a library. See Create
mutagenesis library from existing oligo sets (wizard).
See also
Overview of working with mutagenesis oligo sets
Learn about mutagenic oligos and mutagenesis libraries