Learn about SureSelect Target Enrichment libraries |
|
Target enrichment, also known as genome partitioning, is a method that isolates specific fragments of genomic DNA for sequencing. You use a library of complementary oligonucleotide "baits" to retrieve fragments of interest (target DNA). The target DNA hybridizes well with the baits, but other DNA does not, which forms the basis of a powerful selection method that lets you focus your sequencing efforts.
When you order a SureSelect Target Enrichment library from Agilent, the final product that you receive is a kit that contains a set of biotinylated RNA oligonucleotides. However, as part of the library manufacturing process, Agilent first creates DNA oligonucleotides, and then later transcribes them into RNA. Thus, when you create a library in eArray, you specify bait sequences in terms of DNA bases (A, C, G, T).
With eArray, you can access existing baits and bait libraries or create custom libraries of baits. A bait library is a collection of oligonucleotides in a tube, not a microarray, but you can leverage the well-developed eArray microarray creation infrastructure to easily design and obtain the libraries that you need for your research. To use eArray to create bait libraries, you must be an eArray registered user. When you log in to eArray, you set the application type to SureSelect Target Enrichment, and the relevant tabs and commands appear. When you become a registered user, you also gain access to eArray's large, robust set of microarray creation tools.
Note: You can also use eArray to create libraries that retrieve specific RNAs for sequencing. See SureSelect RNA Enrichment libraries.
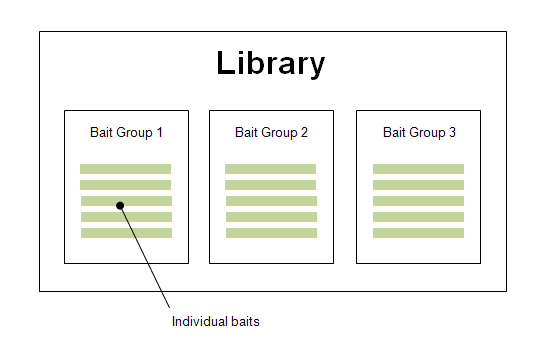
In eArray, bait libraries contain one or more bait groups, and each bait group contains individual baits:

eArray stores individual baits as well as bait groups as separate entities, so you can use them as building blocks to make many different libraries.
For individual baits, you can use existing baits within eArray. To put your own baits on eArray, you can upload them, and you can also use Bait Tiling, a method that creates baits that cover selected regions of a genome of interest at even intervals. eArray supports a bait length of 120 nucleotides.
To organize baits into bait groups, you can select baits based on a Search Your Baits search. You can also create a bait group that contains baits that you upload or those that you create with the Bait Tiling tool. Baits and bait groups are separate entities—you can use an individual bait in any number of bait groups.
One of the easiest ways to design bait libraries is to use one of eArray's built-in Library Wizards. Each wizard leads you step-by-step through the library creation process. As you complete a wizard, you can submit your newly-designed library to Agilent Manufacturing. To obtain the library, you request a quote online through eArray, and then place an order through your Agilent representative. eArray has several Library Wizards:
Create Library by Bait Tiling – Use this wizard to design a library based on oligonucleotides that cover specific regions of the genome of interest at even intervals.
Create Library from Existing Bait Groups – Use this wizard to design a library that includes existing collection(s) (groups) of baits. You can include your own bait groups if they are in your user account on eArray, and you can also include bait groups from the Agilent Catalog.
Create Library from Bait Upload – Use this wizard to create a library based on a file of bait sequences that you upload.
Combine Base and Supplemental Libraries – Creates a combined library that contains a selected Agilent Catalog library (the base library), and a custom supplemental library. This process lets you add baits for regions that are not included in the catalog library. Before you use this wizard, you must first use the Bait Tiling wizard to create a custom supplemental library that contains the desired additional baits.
eArray also gives you other options for libraries:
You can create a custom library manually from bait group search or browse results.
If your desired library already exists within eArray, either in the Agilent Catalog or in a folder to which you have access, you can search or browse for it. You can then submit it to Agilent Manufacturing and request a quote for it or purchase it from the Agilent Online Store through eArray. Search and browse results also give you several other commands that you can use to manage libraries. See Actions you can take on libraries.
You can create a library to be used for multiplexing. Multiplexing is always enabled for certain smaller libraries, and is available as an option for other libraries. You select multiplexing when you request a quote for a library or purchase it from the Agilent Online Store through eArray.
Agilent also offers specialized SureSelectXT kits. These kits, which are based on a given SureSelect Target Enrichment library, offer a complete Target Enrichment workflow for next generation sequencing. See SureSelectXT kits.
If you use the eArrayXD program in Agilent Genomic Workbench to submit libraries to Agilent, these libraries are also available on the eArray Web site. Some restrictions apply. See Search for eArrayXD libraries.
Library capacity and library sets – Currently, eArray supports the 1 X 55K library size, which can accommodate up to 57,750 baits. If you design a custom library that contains more than 57,750 baits, eArray automatically creates a library set, which distributes the requested baits evenly among multiple libraries. Library sets are handled as a single entity. You cannot separately work with or order the individual libraries in a library set. For details, see Library sets.
Bait Boosting – To make genomic fragment pull-down more consistent, Agilent increases the number of copies of both "orphan" and GC-rich baits in Agilent Catalog bait libraries. This process, called bait boosting, is also applied by default to custom libraries that you create in eArray. An orphan bait has no immediate neighbors in the genome within 1 bp on either side of the bait. This can occur when baits are tiled to very short regions, or when repeat or other regions are avoided during the tiling process and one or more short, isolated target regions are created. A GC-rich bait has a GC content of more than 65%. Both orphan and GC-rich baits produce less effective genomic fragment pull-down than other types of baits.
Note:
•
Bait boosting can be removed or applied when you create, edit, or
review a library. Changes to bait boosting can only be made to libraries
with a status of Draft or Review.
•
Bait boosting cannot be directly applied to a combined library. However,
since the base library in a combined library is always an Agilent
Catalog library, bait boosting has already been applied to the base
library. Also, when you create a supplemental library for inclusion
in a combined library, bait boosting is applied by default to the
supplemental library.
•
Agilent does not automatically apply bait boosting to existing custom
libraries that were created in previous versions of eArray that did
not support bait boosting. However, you can apply bait boosting to
these libraries when you edit or
review them.
Library status – As you create a library, it goes through several status changes. When the library has a status of Complete or Submitted, eArray assigns a unique ELID (Enrichment Library ID) number to the library.
If you require greater flexibility, or want to focus your attention on one aspect of the process at a time, eArray lets you do this, as well. See the following topics for more details:
Agilent provides these recommendations for the creation of custom SureSelect Target Enrichment Bait Libraries:
When you use Bait Tiling, avoid repeat regions with fairly high stringency (at most 20 bp overlap).
Use the "Optimized" Bait Tiling strategy. To do so, mark the Use Optimized Parameters check box when you set up a Bait Tiling job. These parameters have been found to work well under standard conditions and are optimized for each available sequencing technology.
The SureSelect Target Enrichment protocol is optimized for capture regions of cumulative size greater than 1 Mb. Therefore, optimal results will be obtained with 1Mb+ captures.
Additional recommendations from Agilent can be found in the topic Bait tiling (SureSelect Target Enrichment). Also, you may find the Agilent tutorials on the SureSelect Target Enrichment application type to be useful. To view these tutorials, go to the eArray Login page. Under Additional Information, click QuikScan Start Tutorials and eArray Viewlets. In the new page that appears, click SureSelect Target Enrichment Tutorial with Wizard or SureSelect Target Enrichment Tutorial without Wizard.
eArray makes it easy for you to work with others down the hall, or across the world. You can create collaborations with others, then work together to construct and submit bait libraries of mutual interest. You create a special collaboration workspace that has many of the same tools as your individual user workspace. See the following topics for more details:
What are the roles in a collaboration